Swedish bearing manufacturer SKF will invest 50 million kronor (US$4.9 million) in a magnetic bearing plant in Tangier, Morocco, to enhance its technology and manufacturing capabilities in magnetic bearings, the company said in a statement on May 22.
The statement said that magnetic bearings are used in turbomachinery and other high-speed applications, such as hydrogen liquefaction and oil-free industrial compressors, and that “the new plant will start operations in the second quarter and when fully operational will help the company to meet the growing demand for magnetic bearings”.
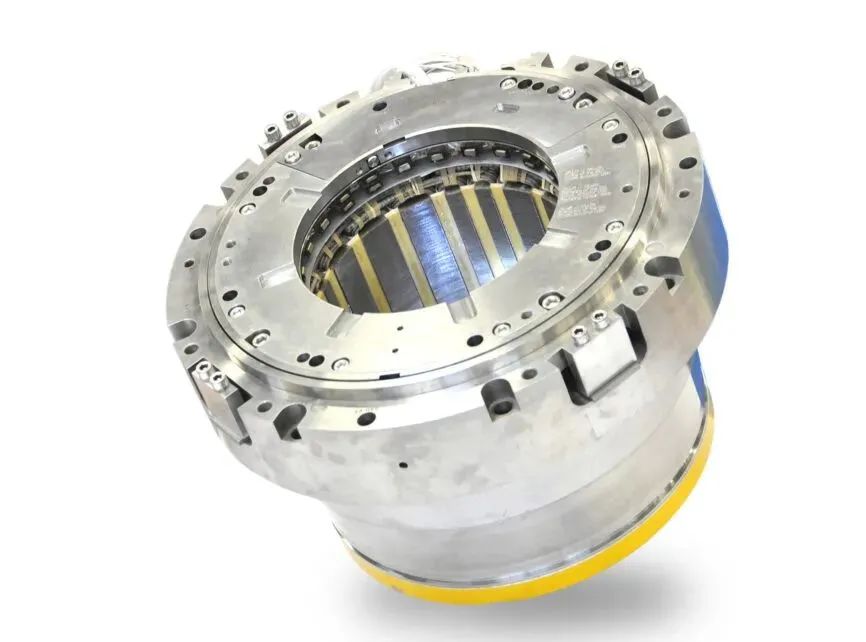

Magnetic bearings are one of SKF’s technology growth areas.
SKF Group has a record order book of more than SEK 1 billion for magnetic bearing products in 2022.
Further reading:
What is a magnetic floating bearing? A magnetic floating bearing, a new type of high-performance bearing, is a form of support that relies on magnetic field forces to support the load or levitate the rotor. Compared to traditional ball bearings, sliding bearings and oil film bearings, magnetic floating bearings do not have mechanical contact and the rotor can reach very high operating speeds, with the advantages of low mechanical wear, low energy consumption, low noise, long life, no lubrication, no oil pollution, etc., especially for high-speed, vacuum, ultra-clean and other special environments.
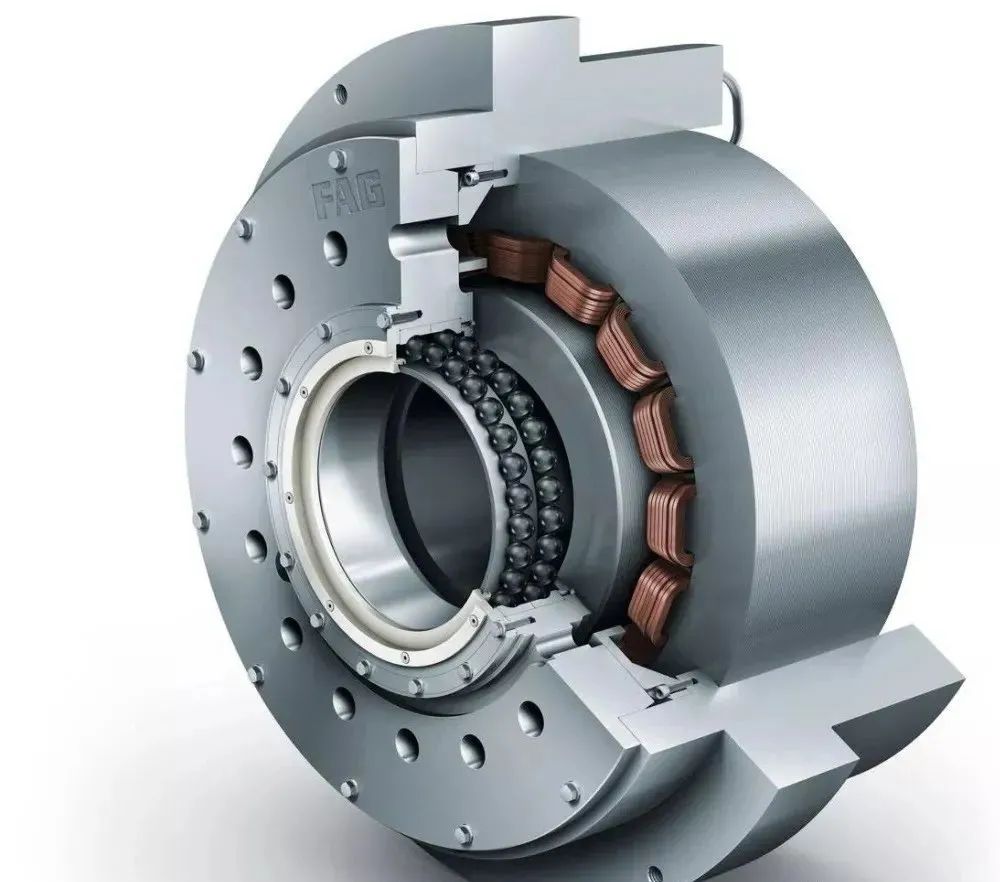

They are widely used in machining, turbomachinery, aerospace, vacuum technology, rotor dynamics identification and testing and are recognised as a promising new type of bearing.

Introduction to magnetic floating bearings
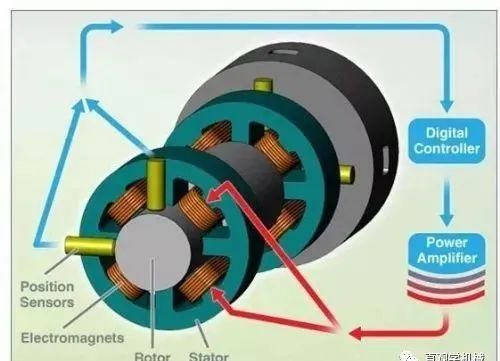
How do magnetic floating bearings work?
The electromagnets are arranged in the form of radial and axial bearings and provide the magnetic pull to lift the spindle of the rotating machine. The current in the solenoid is regulated by a precise digital control cabinet, which provides the magnetic force to keep the spindle well centred in response to changes in the external load at all times. In this way, the shaft is lifted without contact and the bearing stiffness and damping can be adjusted by a digital control cabinet. These features enhance the performance of the high-speed rotating machine and give the machine its distinctive characteristics of high reliability and low energy consumption.
Types of magnetic floating bearings
Magnetic floating bearings are classified according to their control method, source of magnetic energy and form of construction. In addition, they can be classified according to the type of magnetic field as permanent, electromagnet and permanent magnet-electromagnet hybrid. The bearings can also be divided into suction and repulsion types according to the type of suspension force. Superconducting magnetic bearings are also classified as low temperature superconducting and high temperature superconducting.

There are also some special restrictions between the different types in the various classifications above, which should be particularly noted:
① Permanent magnet type bearings can only be passive type (passive type), and passive type bearings cannot be stable in all 3 directions, at least 1 direction should be active type. ②DC excitation type bearing can only be active type (active type). ③ pure electromagnet type bearing can only be 5 degrees of freedom control type bearing, its volume, mass and power consumption are relatively large. ④Repulsive type magnetic bearing, due to the low utilization rate of magnetic force, the structure is more complex than the suction type, generally rarely used.
Features of magnetic floating bearings
(1) No contact, no wear, no lubrication:When the magnetic levitation bearing works, it is in a suspended state, no contact between the relative moving surfaces, no mechanical friction and contact fatigue, which solves the problem of unit component loss and replacement. At the same time, a series of devices such as lubrication systems are omitted, which saves space and does not have the problem of environmental pollution caused by the aforementioned devices.
(2) Low vibration, low noise and low power consumption: The magnetic levitation bearing rotor avoids the large vibration and high decibel noise caused by the contact collision of traditional bearings during operation, which improves stability, reduces maintenance costs and extends its service life, while the low power consumption of the suspended magnetic levitation bearing is only 6%-25% of the power consumption of traditional mechanical bearings. At a speed of 10,000r/min, its power consumption is only about 15% of that of a mechanical bearing.
(3) High speed, high precision, high reliability: allowing the rotor to rotate at high speed, its speed is mainly limited by the strength of the material, it can work under supercritical, hundreds of thousands of revolutions per minute conditions, and the rotor’s rotary accuracy has reached micron level or even higher, which is far from the speed and accuracy of ordinary mechanical bearings, and the reliability of electronic components is largely higher than traditional mechanical parts.
(4) Controllability, online working condition monitoring, testable diagnosis:We can control the static and dynamic performance of the maglev bearing online. In fact, the system itself integrates monitoring of working conditions, fault diagnosis and online regulation.
Technical analysis
As technology continues to advance and develop, the performance of maglev bearings is constantly being improved, while the integration of electronic components is driving down their cost year on year. Although maglev products have been successfully used in many fields after years of exploration at home and abroad, there are still many challenges in this technical field, such as the optimised design of the control system and the dynamic characteristics of the material rotor shaft system. In order to improve the control methods and strategies more effectively, it is necessary to focus on the dynamics of the rotor system in parallel with the in-depth study of the control system in order to achieve the ideal control of complex rotors.
At present, most air conditioning fans use mechanical bearings, which generate mechanical friction between the fan spindle and the bearings, and the motor must overcome this friction in order to drive the rotating blades, while causing the motor to heat up and generate large vibrations, making the fan life reduced. To achieve long fan operation, bearing lubrication system and cooling system improvements are also required. If the magnetic floating bearing is used, there is no mechanical friction between the stator and rotor, the magnetic floating bearing has zero running resistance and does not heat up, thus eliminating the need for cooling systems and lubrication systems, reducing the volume and weight, improving reliability and life, and the suspended operation greatly reduces the mechanical noise and also greatly reduces the mechanical vibration, the vibration amplitude is much smaller than that of ordinary fans, improving the stability of the whole air conditioner.
From the current level of domestic magnetic floating bearing technology, although the conditions for application in ambient temperature equipment, there are still two aspects of the problem: on the one hand, it is difficult to achieve high precision control of the magnetic suspension bearing rotor, thus resulting in poor system reliability and high failure rate; on the other hand, the lack of standardised product technology.
Economic analysis
The realisation of the various advantages of magnetically suspended bearings described above is based on a complex electronic control system. Because of the high cost of the sensors, which form an important part of the system, and the design costs of the control system, the overall cost is tens of times higher than that of an ordinary mechanical bearing, which largely limits its application and promotion in industry.
In the long run, the high energy consumption of traditional fans and pumps, which account for a large proportion of the overall energy consumption, and the long working runs, with expensive electricity costs, especially in the middle and later stages of maintenance and losses are particularly noticeable, leading to increased energy consumption as well as expenditure for the whole system. The use of magnetic floating bearings also saves on the configuration costs of some devices, such as lubrication systems, gear drives, cooling systems, etc. When converted into the cost of magnetic floating bearings, the amount is considerable.